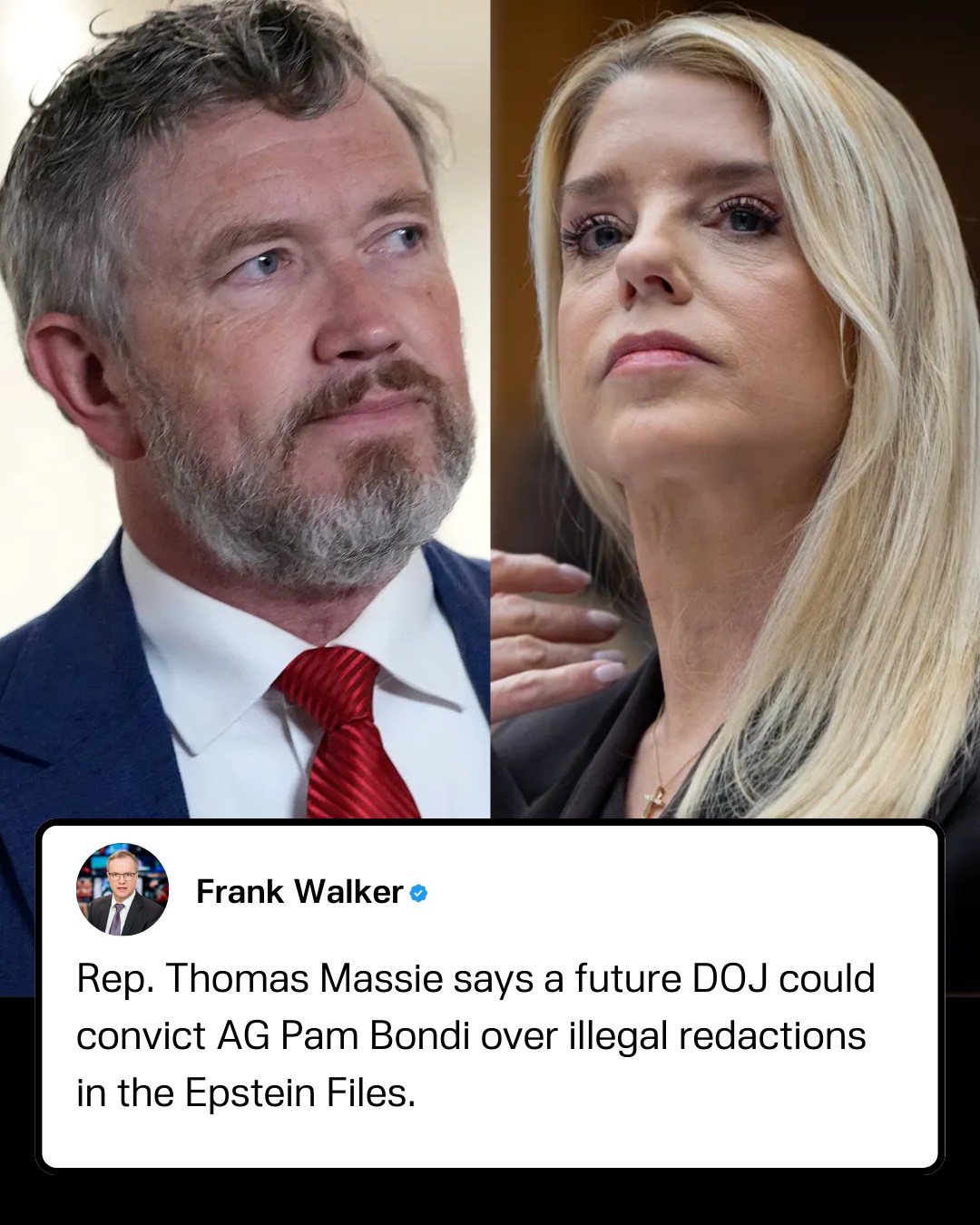
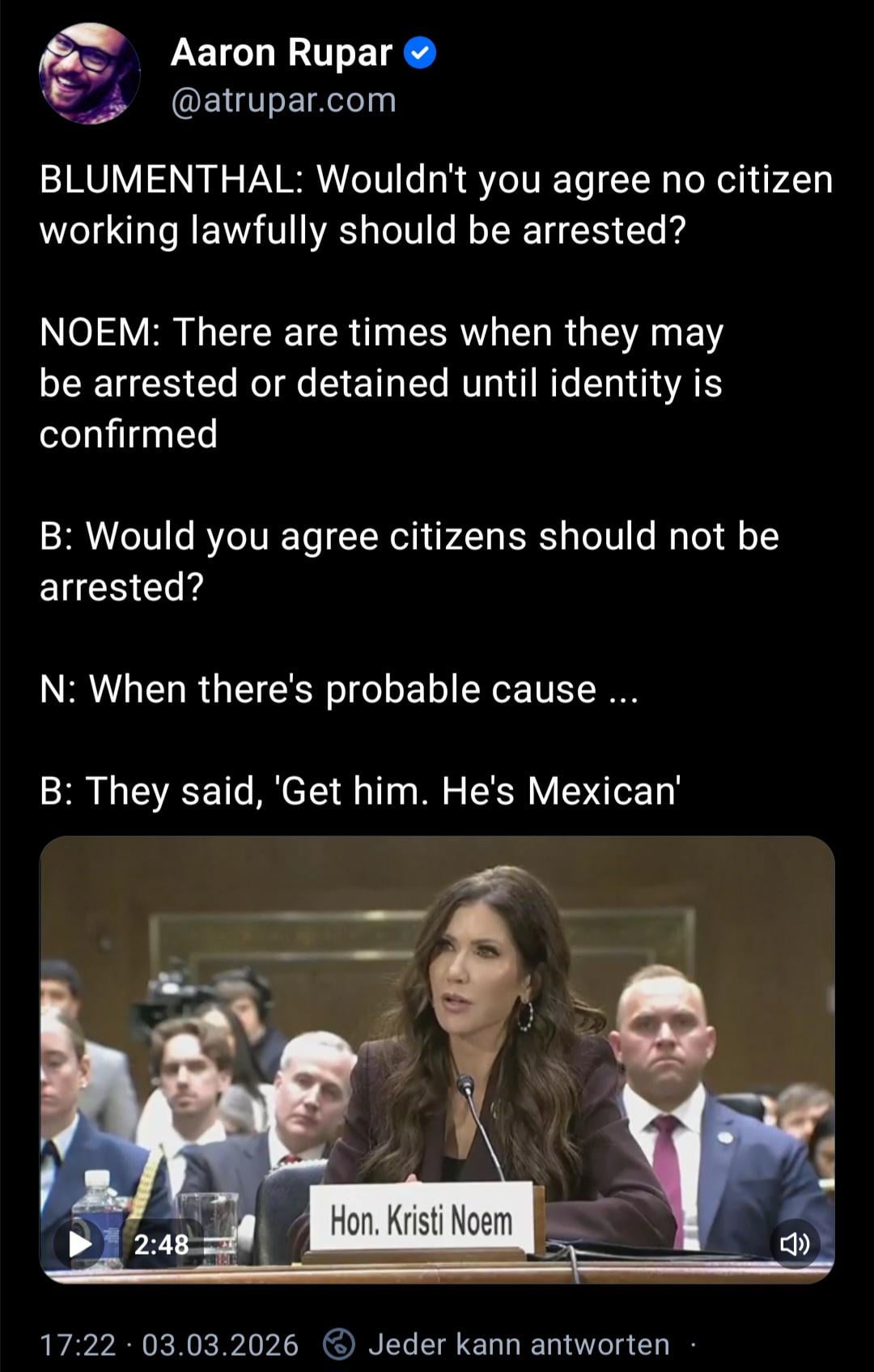
Representative Ted Lieu has reportedly referenced newly released Epstein-related documents while calling for full transparency and accountability, adding fresh political pressure amid an already volatile moment for the White House. The renewed focus on the Epstein files comes as the United States faces escalating tensions in the Middle East, intensifying debate at home over national security decisions and political leadership. Public opinion remains deeply divided, with some critics questioning the timing of foreign policy moves and others arguing that military actions are driven strictly by strategic considerations.
At the same time, global rhetoric has sharpened, with international figures issuing stark warnings about the risks of further escalation. Reports of shifting military assets, strained alliances, and concerns over nuclear oversight have added to the sense of uncertainty, while lawmakers across party lines continue to clash over transparency, accountability, and the broader direction of U.S. policy. As these parallel crises unfold, domestic political scrutiny and high-stakes geopolitical tensions are colliding in ways that are fueling intense national and international attention.
#EpsteinFiles #USPolitics #NationalSecurity #Geopolitics #BreakingNews
At the same time, global rhetoric has sharpened, with international figures issuing stark warnings about the risks of further escalation. Reports of shifting military assets, strained alliances, and concerns over nuclear oversight have added to the sense of uncertainty, while lawmakers across party lines continue to clash over transparency, accountability, and the broader direction of U.S. policy. As these parallel crises unfold, domestic political scrutiny and high-stakes geopolitical tensions are colliding in ways that are fueling intense national and international attention.
#EpsteinFiles #USPolitics #NationalSecurity #Geopolitics #BreakingNews
Representative Ted Lieu has reportedly referenced newly released Epstein-related documents while calling for full transparency and accountability, adding fresh political pressure amid an already volatile moment for the White House. The renewed focus on the Epstein files comes as the United States faces escalating tensions in the Middle East, intensifying debate at home over national security decisions and political leadership. Public opinion remains deeply divided, with some critics questioning the timing of foreign policy moves and others arguing that military actions are driven strictly by strategic considerations.
At the same time, global rhetoric has sharpened, with international figures issuing stark warnings about the risks of further escalation. Reports of shifting military assets, strained alliances, and concerns over nuclear oversight have added to the sense of uncertainty, while lawmakers across party lines continue to clash over transparency, accountability, and the broader direction of U.S. policy. As these parallel crises unfold, domestic political scrutiny and high-stakes geopolitical tensions are colliding in ways that are fueling intense national and international attention.
#EpsteinFiles #USPolitics #NationalSecurity #Geopolitics #BreakingNews