NASA and IBM Unveil AI That Helps Scientists Forecast Solar Storms
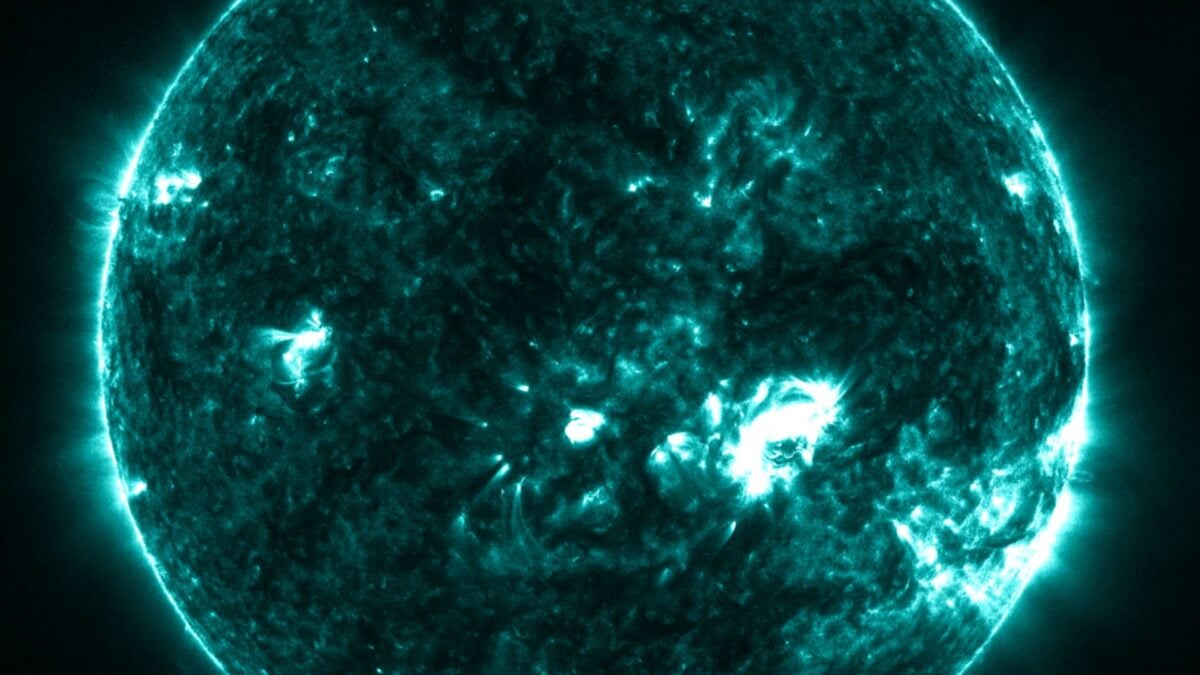
Earlier this year, local and national officials gathered for a first-of-its-kind tabletop exercise to test their readiness for a severe solar storm. The simulation exposed major gaps in scientists’ ability to forecast space weather, which threatens critical infrastructure on Earth and in orbit.
On Wednesday, August 20, IBM and NASA unveiled Surya: an open-source AI model that could begin to fill those gaps. Heliophysicists currently rely on complex computer models to monitor and predict the Sun’s activity. Surya improves upon the lead time and accuracy of existing solar forecasting technologies, allowing scientists to not only predict a solar flare two hours out but also visually pinpoint where it should occur on the Sun’s surface, according to IBM.
“It’s very important to have a mechanism to look into the Sun and understand how these events [are going to happen], when they’re going to happen, why they’re going to happen, and start predicting the occurrence so that we can be prepared,” Juan Bernabé-Moreno, director of IBM Research Europe for Ireland and the U.K., told Gizmodo.
The hazards of solar weather
The surface of the Sun is a violent place. Our host star is constantly emitting bursts of energy such as solar flares, high-speed solar winds, and coronal mass ejections. When Earth is in the line of fire during one of these events, the onslaught of high-energy particles can trigger a geomagnetic storm in the upper atmosphere. Such storms result from disturbances in Earth’s magnetic field and can damage or disrupt satellites, power grids, and radio communication systems, according to NASA.
Being able to anticipate these outbursts gives decision-makers critical lead time to protect vulnerable infrastructure, potentially avoiding billions of dollars in damage. According to a systemic risk analysis by Lloyd’s, a severe solar storm could result in losses to the global economy of $2.4 trillion over a five-year period.
Forecasting flares with Surya
Bernabé-Moreno thinks of Surya as a powerful AI telescope that also lets you look into the future. Whereas traditional solar weather prediction relies on partial satellite views of the Sun’s surface, Surya trained on nine years of high-resolution solar observation data gathered by NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory. This telescope launched in 2010 and has been continuously observing the Sun for the past 15 years, capturing images every 12 seconds at various wavelengths to take the temperature of its layers and map magnetic activity.
Heliophysicists will be able to use Surya in a variety of ways, but its most novel application is solar flare prediction, IBM senior research scientist and technical project lead Johannes Schmude told Gizmodo in an email. The model does this by generating an image of an event that the SDO satellite is likely to see, essentially predicting what the surface of the Sun will look like hours ahead.
Testing showed that Surya can predict a solar flare two hours in advance with a 16% improvement in flare classification accuracy, but IBM is exploring the accuracy of even longer lead time predictions, according to Schmude. It’s important to note, however, that Surya trained on data from the previous solar cycle. “Testing the model’s applicability to Solar cycle 25 is one of the post-release tasks on our list, but we plan to explore continuous training and other fine-tuning with data from Solar Cycle 25,” Schmude said.
Following the release of this open-source AI model, Bernabé-Moreno is excited for the scientific community to begin using it on a wider scale, identifying new applications and challenging its capabilities. “That is going to create utility,” he said. “That, for us, is the most important thing.”



- CỘNG ĐỒNG
- News
- Tech
- Food
- Causes
- Personal
- Art
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Games
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Science
- Networking
- Party
- Religion
- Fashion
- Sports
- Stars
- Xã Hội


